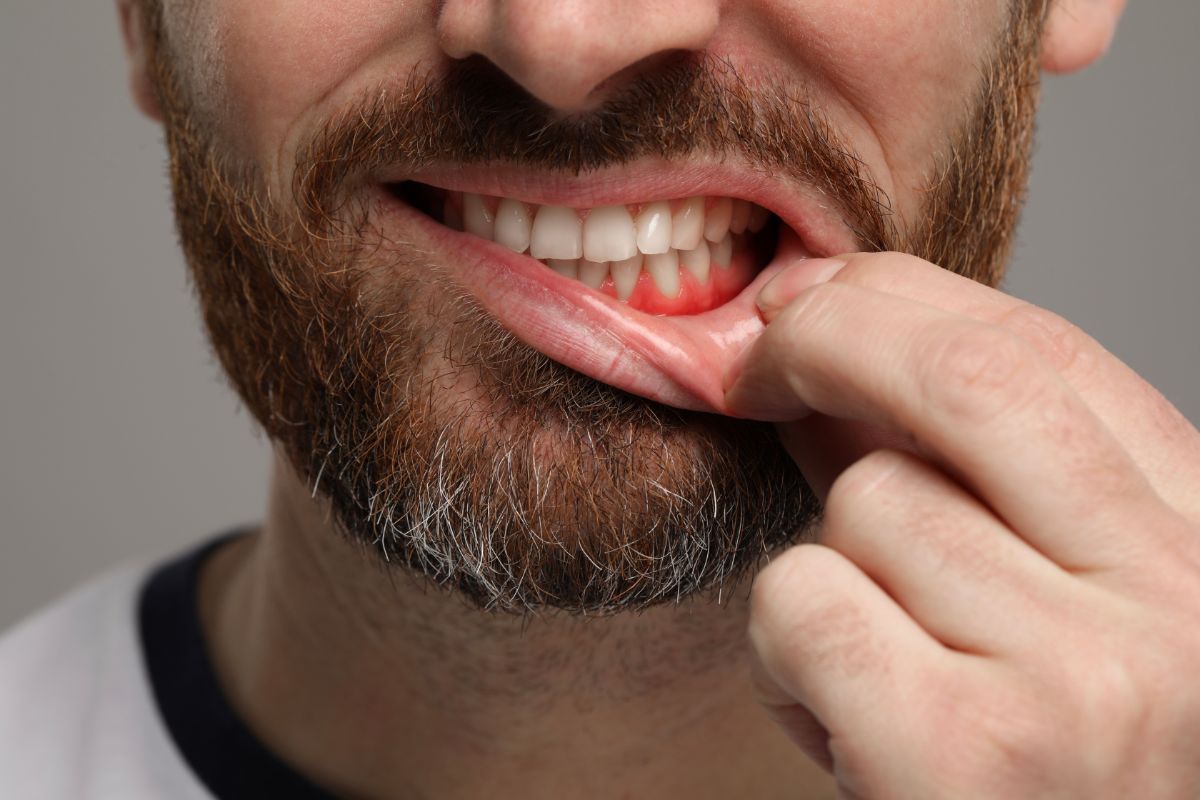
What is Gum Disease?
The first stage of gum disease is gingivitis. Gingivitis is the inflammation of gums. When plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the surfaces of the teeth and gums—is not removed on time, it can harden into tartar, which irritates the gums, causing bleeding and inflammation. The bacteria in plaque release acids that attack your teeth layer by layer, leading to tooth decay.
This occurs when you forget or deliberately skip brushing, flossing, rinsing, and general oral hygiene. It takes about 72 hours for plaque to calcify into tartar (calculus), which deposits along the gum line and makes it difficult to clean your teeth and gums thoroughly. Over time, this build-up causes gum irritation and inflammation, resulting in gingivitis.
In the more advanced stage of gum disease, called periodontitis, the inner layer of the gums and bone begins to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets. These tiny spaces trap food debris and bacteria, leading to infection. The immune system attempts to fight the bacteria, but plaque continues to spread below the gum line. If untreated, the supporting bone and tissues are destroyed, which may ultimately result in tooth loss.
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
- Gingivitis: Initial stage of gum disease – symptoms include red or swollen gums and bleeding when brushing or flossing. If untreated, it may progress to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis: Advanced stage of gum disease – symptoms include loose teeth and exposure of the tooth’s root. If untreated, it may lead to tooth loss.
What is the Solution?
The answer is simple: Cleaning, cleaning, cleaning! Known as Scaling, this professional cleaning procedure—performed every 6 months along with a routine dental check-up— can significantly prevent or reduce the incidence of gum disease. It is also the first line of treatment when gum disease is detected.
Scaling involves the dentist removing all plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) from above and around the gum line. In more severe cases, a deeper cleaning is performed to ensure the entire pocket, down to the bottom, is completely cleaned.
Are You at Risk of Gum Disease?
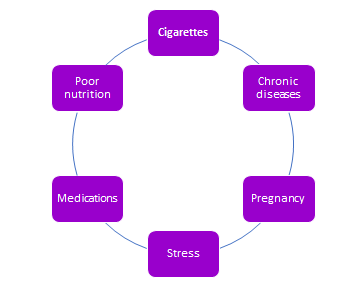
- Smoking or tobacco use is one of the biggest risk factors and reduces the chances of successful treatment. Smokers are twice as likely to develop gum disease as non-smokers.
- Stress weakens the body’s ability to fight infection, including gum disease.
- Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause, make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Poor nutrition deprives the body of essential nutrients needed to fight infection, including gum disease.
- Certain medications for various health conditions can affect oral health and should always be communicated to your dentist.
- Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and HIV weaken the immune system, increasing vulnerability to gum disease. These conditions must be disclosed to the dentist.
Worried about gum disease?
Book a consultation with our dentists to protect your smile and restore your gum health.
